SP_RampUP Logic Block Documentation
Overview
The fn_SP_RampUP function block is designed to smoothly increase a set point (SP) from its current value to a desired target over a predefined time period. This is especially important in automation systems where sudden jumps in set point can lead to system instability, overshoot, or even equipment damage.
By utilizing the fn_SP_RampUP block, the increase is linear, controlled, and safe, ensuring system integrity during ramp transitions.
In the above picture we are showing the fn_SP_RampUP block.
Functional Description
- This block gradually ramps up the set point over the time duration defined by
TM_PT. - It ensures a predictable and smooth transition from the initial to the target set point.
- Once the target is reached, the output
FinishbecomesTRUE, signaling the completion of the ramp-up process.
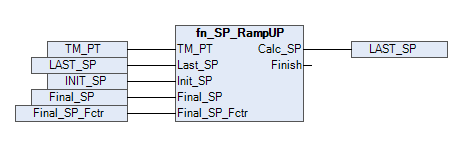
Here is an illustration showing how the block behaves with real-time data and calculated outputs.
Signal Connection Example
Below is a typical example showing how the pins are connected to the fn_SP_RampUP block within a control logic diagram.
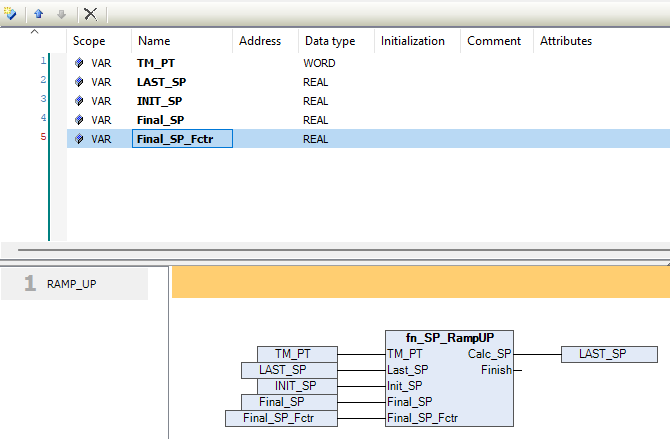
In the above picture we are showing the example of connecting the pins.
Pins Information
| Signal Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
TM_PT |
WORD |
Time duration over which the set point will be increased |
Last_SP |
REAL |
The previous set point value before ramping started |
Init_SP |
REAL |
The current initial set point from which ramping begins |
Final_SP |
REAL |
The desired target set point after ramping |
Final_SP_Fctr |
REAL |
A multiplier applied to the target set point for scaling (use 1.0 for exact) |
Calc_SP |
REAL |
The intermediate set point calculated during the ramp-up |
Finish |
BOOL |
FALSE = Ramp-up not completed, TRUE = Ramp-up cycle completed |
Operational Behavior
-
Initialization:
The block readsInit_SPas the starting point and calculates the final target usingFinal_SP × Final_SP_Fctr. -
Ramping:
It linearly increasesCalc_SPover time, based onTM_PT, moving fromInit_SPto the scaledFinal_SP. -
Completion:
Once the target set point is reached, theFinishsignal becomesTRUE, indicating ramping is done.
Example Use Case
For instance, in a flow control application, where the pump speed needs to be increased gradually over 10 seconds, set TM_PT = 10, Init_SP = 0.0, Final_SP = 100.0, and Final_SP_Fctr = 1.0.
This allows a smooth and safe increase in flow rate, avoiding system shocks.
Best Practices
- Choose
TM_PTappropriately based on how quickly the system can respond without oscillations. - Set
Final_SP_Fctr = 1.0if no scaling ofFinal_SPis required. - Reset and update
Init_SPandLast_SPcorrectly each time the ramping is triggered. - Use the
Finishoutput to trigger downstream logic only after the set point has reached the desired value. - Ideal for applications such as temperature increases, motor start ramps, gradual pressure build-up, etc.
The
fn_SP_RampUPblock provides a structured and safe way to implement set point ramp-up functionality, minimizing disturbances and ensuring a smooth and reliable process transition.