MOTOR_REV Logic Block Documentation
Overview
The MOTOR_REV function block is designed to control motors that require both forward and reverse operations. It facilitates the safe starting, stopping, direction switching, and health monitoring of motors within an industrial automation environment.
This block is essential for machinery where direction control is required, such as conveyors, hoists, or certain types of pumps.
Logic Block Illustration
The MOTOR_REV block provides:
- Bidirectional Motor Control: Supports start/stop logic for both forward and reverse operation.
- Auto/Manual Mode Handling: Enables switching between automatic and manual control modes.
- Safety and Permissive Checks: Executes interlock and permissive logic separately for forward and reverse directions.
- Feedback Monitoring: Monitors run feedbacks for both directions and uses timers to detect abnormal conditions.
- Runtime Monitoring: Tracks motor run hours and provides hardware interface signals for diagnostics.
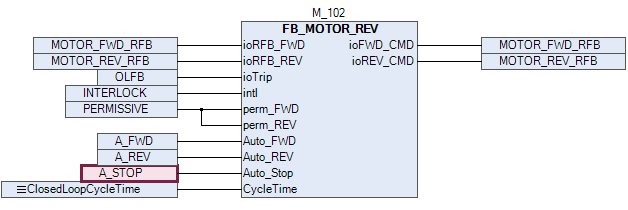
Showing the MOTOR block in the above picture.
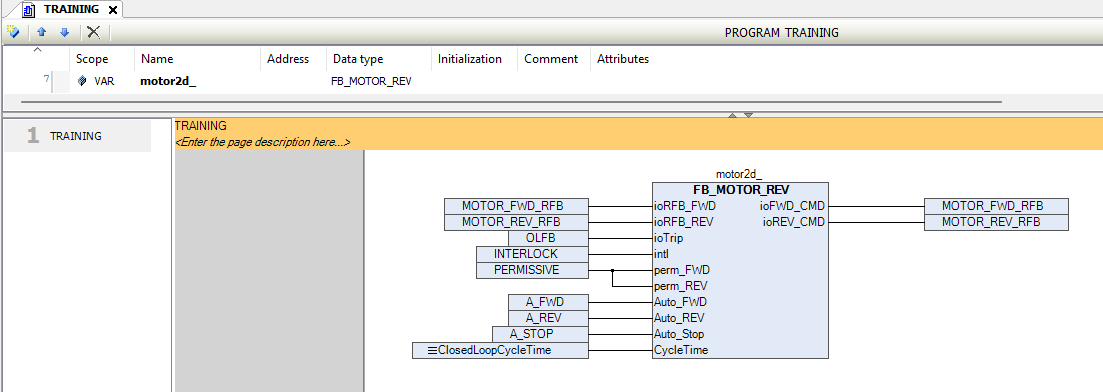
The above picture shows how the inputs and outputs are connected in the MOTOR block.
Input and Output Parameters
| Signal | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
ioRFB_FWD |
BIT |
Motor forward run feedback signal |
ioRFB_REV |
BIT |
Motor reverse run feedback signal |
ioTrip |
BOOL |
Motor trip feedback (fault detected) |
intl |
BIT |
Interlock condition (shared) |
perm_FWD |
BIT |
Permissive condition for forward operation |
perm_REV |
BIT |
Permissive condition for reverse operation |
Auto_FWD |
BIT |
Automatic command for forward operation |
Auto_REV |
BIT |
Automatic command for reverse operation |
Auto_STOP |
BIT |
Automatic stop command |
CycleTime |
BIT |
Cycle time signal for closed loop control |
Start_FWD |
BIT |
HMI start command for forward direction |
Start_REV |
BIT |
HMI start command for reverse direction |
Stop |
BIT |
HMI stop command |
ioFWD_CMD |
BIT |
Forward run command output |
ioREV_CMD |
BIT |
Reverse run command output |
Run_fb_Timer |
REAL |
Wait time for receiving run feedback after command |
Mode |
BOOL |
FALSE = Manual, TRUE = Auto mode selection |
HMI_Interface_hardware |
WORD |
Interface message code for hardware-related messages on HMI |
Run_Time |
REAL |
Total motor run time in hours |
IntlBypass |
BIT |
Interlock bypass switch |
PermBypass_FWD |
BIT |
Bypass forward permissive |
PermBypass_REV |
BIT |
Bypass reverse permissive |
TagName |
STRING(10) |
Tag name identifier for this motor |
Desc |
STRING(12) |
Description of the motor |
Operational Behavior
Auto Mode Behavior
- In Auto mode (
Mode = TRUE): - Motor runs forward if
Auto_FWD = TRUE,perm_FWD = TRUE, and no interlock. - Motor runs reverse if
Auto_REV = TRUE,perm_REV = TRUE, and no interlock. - If
Auto_STOP = TRUE, the motor is stopped.
Manual Mode Behavior
- In Manual mode (
Mode = FALSE): Start_FWDorStart_REVinitiates motor operation in respective direction.Stophalts any current motor operation.
Safety Handling
- The motor runs only when:
- Interlocks are inactive (
intl = FALSE) or bypassed (IntlBypass = TRUE) - Direction-specific permissives (
perm_FWDorperm_REV) are valid or bypassed
Feedback and Diagnostics
- If motor does not start after command within
Run_fb_Timer, fault is flagged. - Interface messages are pushed to HMI via
HMI_Interface_hardwarefor user alerts.
Best Practices
- Configure
Run_fb_Timerappropriately based on your motor's expected startup time. - Enable bypass only during commissioning or manual override scenarios.
- Separate control and HMI logic should monitor
ioRFB_FWDandioRFB_REVto reflect real motor status. - Use
DescandTagNameto provide clear and descriptive motor identity on HMI. - Regularly check
Run_Timeto monitor wear and schedule preventive maintenance.
Summary
The MOTOR_REV block adds directional intelligence and flexibility to motor control within industrial environments. With support for both manual and automated operations, dual-direction logic, comprehensive safety checks, and HMI diagnostics, it ensures a reliable and operator-friendly motor management strategy.
Designed for high-precision motor applications requiring controlled forward/reverse operations, with built-in safety, feedback, and runtime tracking.