Analog Output (AO) Module – Wiring Diagram
INTRODUCTION
This guide covers wiring and setup of the AO-16-G4/8 Analog Output Module. It delivers precise analog signals to control devices such as VFDs and actuators, ensuring smooth and reliable operation within Saksham PLC systems.
AO-16-G4/8 Analog Output Module – Wiring Description
What is an AO Module?
This 16-channel analog output module offers precise control, high signal integrity, and galvanic isolation—enhancing system efficiency, reliability, and productivity in complex PLC applications.
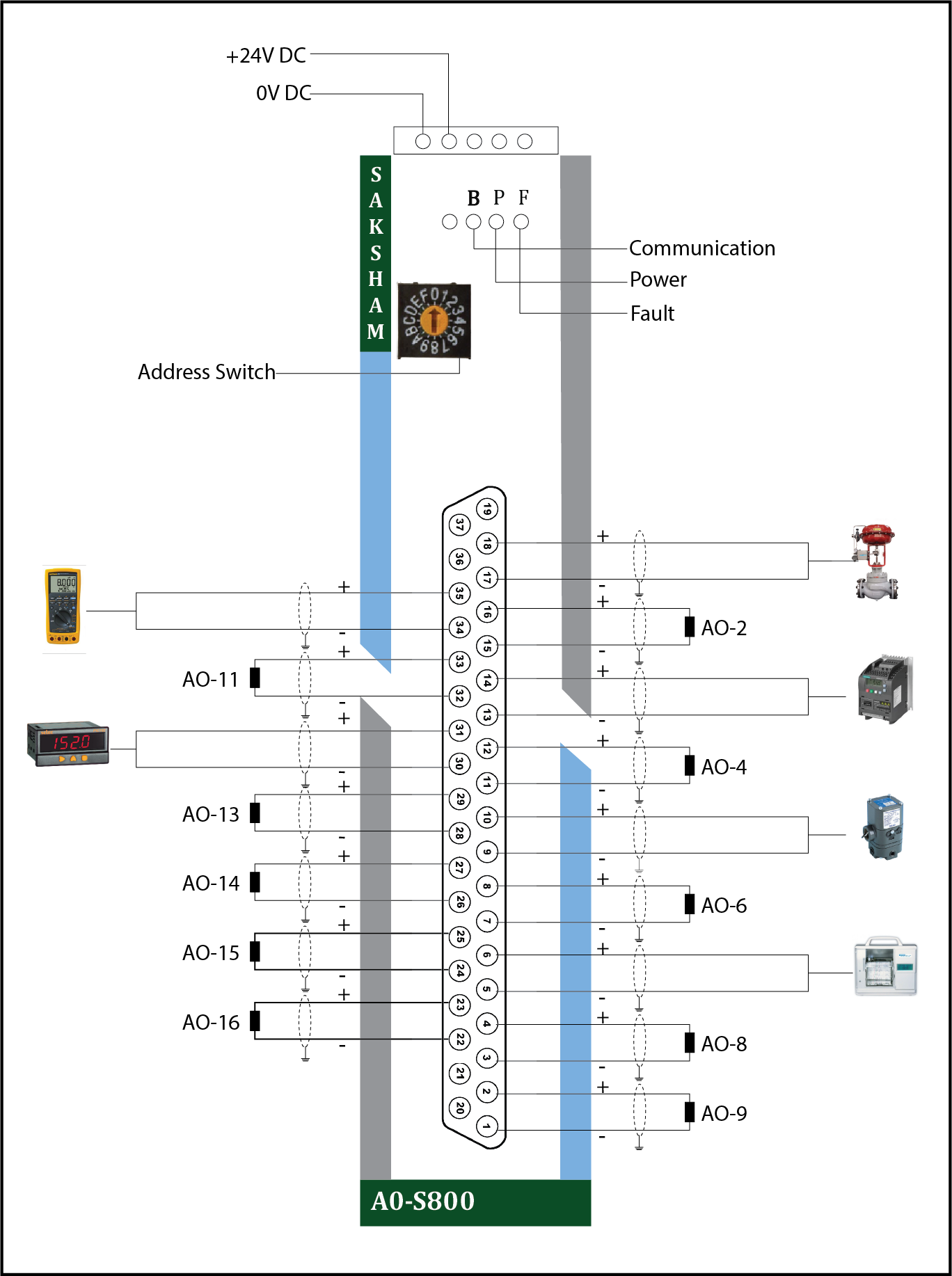
Channel-to-Device Mapping
| Channel | Connected Device |
|---|---|
| AO-2 | Control Valve |
| AO-4 | VFD (Drive) |
| AO-6 | Field Indicator |
| AO-8 | Display Panel |
| AO-9 | Multifunction Transmitter |
| AO-11 | Temperature Indicator |
| AO13~16 | Other analog-controlled devices |
Key Features
- Supports 16 Analog Output channels
- Each output channel provides a separate analog signal to an individual field device
- Typically used for analog control of actuators or display devices
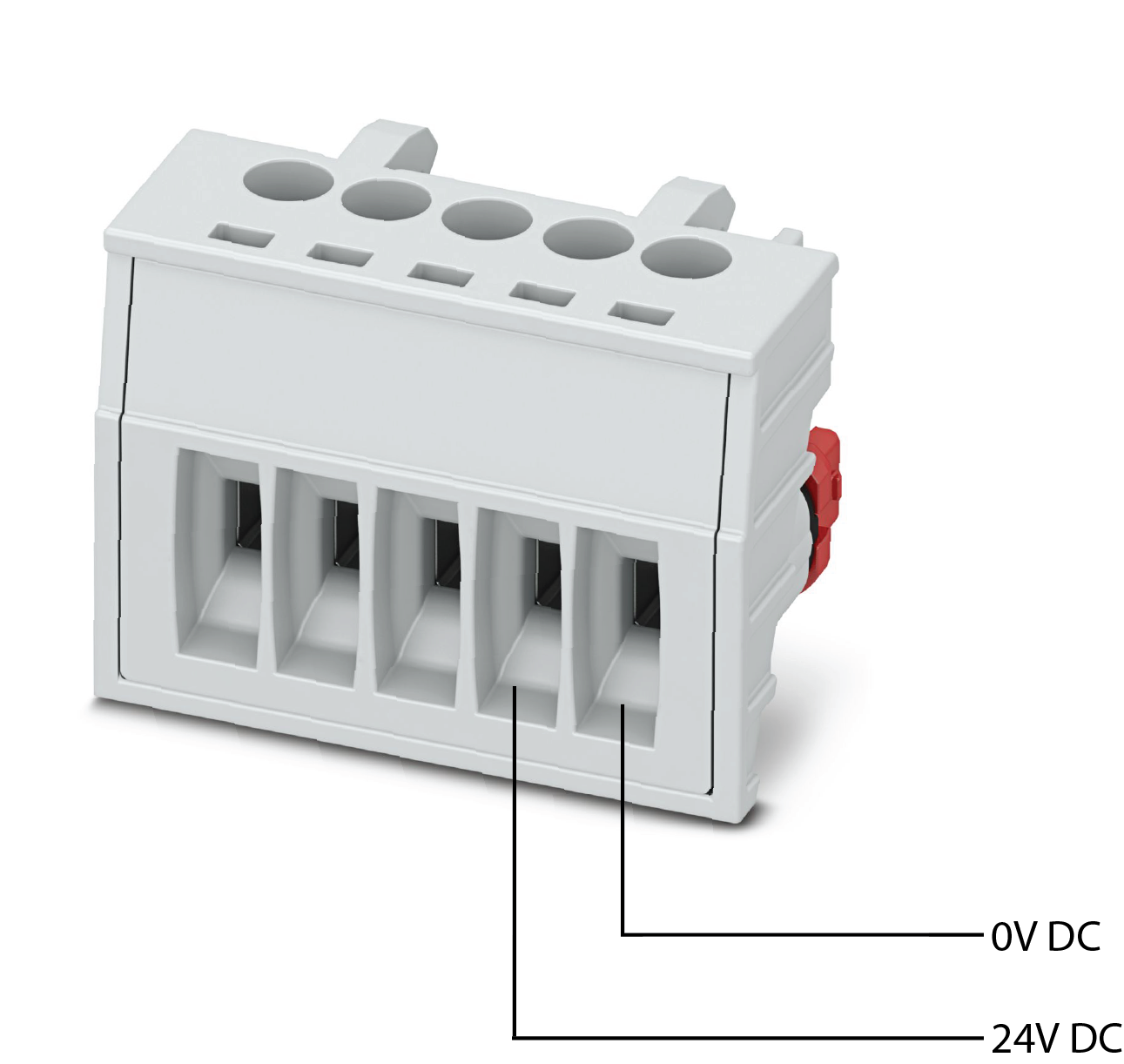
Power Connection
-
Connect a regulated 24VDC power supply to the top power terminals - +24VDC Power supply positive and 0VDC Power supply negative (ground)
-
Output Device Wiring (like control valves, VFDs, displays)
-
Each AO Output channel has two terminals - One for (+) signal and One for (−) return
Follow these steps:
-
Identify the correct channel (e.g., AO1, AO2...AO16).
-
Connect the + terminal of the AO channel to the positive input of the device.
-
Connect the − terminal of the AO channel to the negative/return input of the device.

✅ Ensure signal compatibility between PLC output (e.g., 4–20 mA) and device input.
LED Indicators
- B (Communication): Blinks when communicating with IM, steady glow when not communicating.
- P (Power): Glows when power is ON.
- F (Fault): Glows when a fault occurs.
Wiring Tips
- Use shielded twisted pair cables to avoid noise.
- Route analog wiring away from power or digital lines.
- Strip wire insulation ~7 mm and use ferrules if possible.
- Tighten screws to 0.5–0.6 Nm torque.
Address Switch Configuration
What is an Address Switch?
The Address Switch is a built-in rotary switch on the Saksham module. Its purpose is to assign a unique identification number (address) to the module. This address allows the system's Interface Module (IM) or CPU to correctly identify and communicate with the module over the backplane (TBUS).
Each module in the system must have a distinct address to ensure proper data flow and avoid conflicts.
How Does the Address Switch Work?
- The address you assign using the switch must match the module address configured in your PLC program.
- You set the switch by rotating it using a small screwdriver.
Example Mapping:
| Module Address | Hex Value | Rotary Switch Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 03E8 | 0 |
| 2000 | 07D0 | 1 |
| 3000 | 0BB8 | 2 |
| 4000 | 0FA0 | 3 |
| 5000 | 1388 | 4 |
| 6000 | 1770 | 5 |
| 7000 | 1B58 | 6 |
| 8000 | 1F40 | 7 |
📝 Note: The system reads this hardware address during startup or communication initialization to map and manage each module correctly.
⚠️ Important Guidelines:
- Ensure each module has a unique address — duplicate addresses can cause communication failures.
- After setting the address, verify that it matches your software configuration.
Safety & Best Practices
- Avoid shorting output terminals
- Double-check wiring against diagrams
- Properly label all connected cables for troubleshooting