SP_RampDN Logic Block Documentation
Overview
The fn_SP_RampDN function block is designed to smoothly decrease a set point (SP) from its current value to a target value over a predefined duration. This is especially useful in process control systems where sudden changes to the set point could cause instability or stress to the system.
By employing the fn_SP_RampDN block, the reduction is controlled, systematic, and safe, thereby protecting equipment and improving the overall reliability of operations.
 In the above picture we are showing the fn_SP_RampDN block
In the above picture we are showing the fn_SP_RampDN block
Functional Description
- This block gradually ramps down the set point based on the time period defined by
TM_PT. - It ensures a linear and predictable transition from the initial set point to the required set point.
- When the target is achieved, the output
Finishis set toTRUE.
Here is an illustration showing how the block behaves with real-time data and calculated outputs.
Signal Connection Example
Below is a typical example showing how the pins are connected to the fn_SP_RampDN block within a control logic diagram.
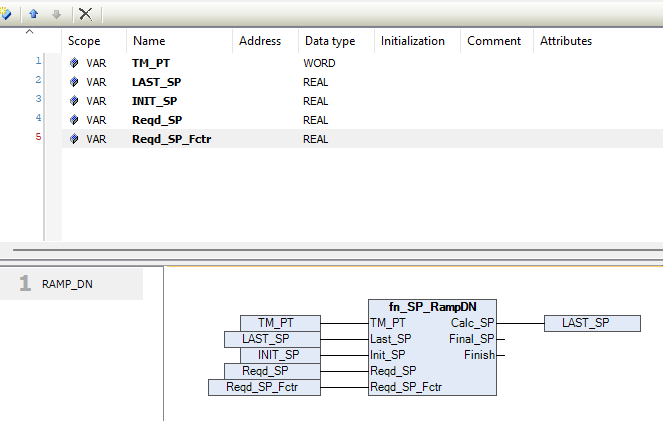
Pins Information
| Signal Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
TM_PT |
WORD |
The period required for the set point to reach the target |
Last_SP |
REAL |
The last known set point value before ramping begins |
Init_SP |
REAL |
Current set point from which the ramping down will start |
Reqd_SP |
REAL |
Desired final set point after ramping |
Reqd_SP_Fctr |
REAL |
Factor applied to scale the required set point (e.g., for percentage reduction) |
Calc_SP |
REAL |
Intermediate calculated set point based on elapsed ramping time |
Final_SP |
REAL |
Final set point once ramping is complete |
Finish |
BOOL |
Status output: TRUE when ramping is complete, otherwise FALSE |
Operational Behavior
-
Initialization:
On activation, the block reads theInit_SPas the starting point and calculates the target value usingReqd_SP × Reqd_SP_Fctr. -
Ramping:
The block gradually reduces the set point fromInit_SPto the scaledReqd_SPover the period defined inTM_PT. -
Completion:
Once the calculated time has elapsed and theFinal_SPis reached, theFinishoutput is set toTRUE.
Example Use Case
For instance, in a temperature control system, you might want to reduce the heater’s set point gradually over 5 minutes to prevent sudden cooling, which could impact product quality. Setting TM_PT = 300 (5 minutes in sec) with appropriate Init_SP and Reqd_SP values would accomplish this smoothly.
Best Practices
- Always provide accurate
TM_PTbased on system dynamics to avoid overshooting or undershooting. - Use
Reqd_SP_Fctr = 1.0if no scaling ofReqd_SPis needed. - Ensure that
Last_SPandInit_SPare consistently updated per cycle for accurate ramping. - Monitor
Finishoutput to trigger subsequent control steps only after ramp-down is complete. - This block is ideal for PID transitions, flow rate reductions, energy-saving shutdown procedures, etc.
The
fn_SP_RampDNblock offers a structured and safe method to implement set point ramp-downs, minimizing system instability and ensuring a smooth transition to the desired target values over a time-controlled ramp period.